Cutting through a material as strong as plate steel requires specialized machinery and training. The appropriate technique for a job depends on the project’s budget, specifications, and production schedule. The pros at Pennsylvania Steel Co. prioritize these specific needs to ensure only high-quality results and 100% customer satisfaction. In this guide, they cover the primary methods and safety tips to know when planning how to cut steel plate.
4 Main Methods for Cutting Steel Plate
Those wondering how to cut steel plate and achieve the desired result while avoiding injury must consider the significant differences between each technique. Most fabricators cut steel plates using one of four primary methods:
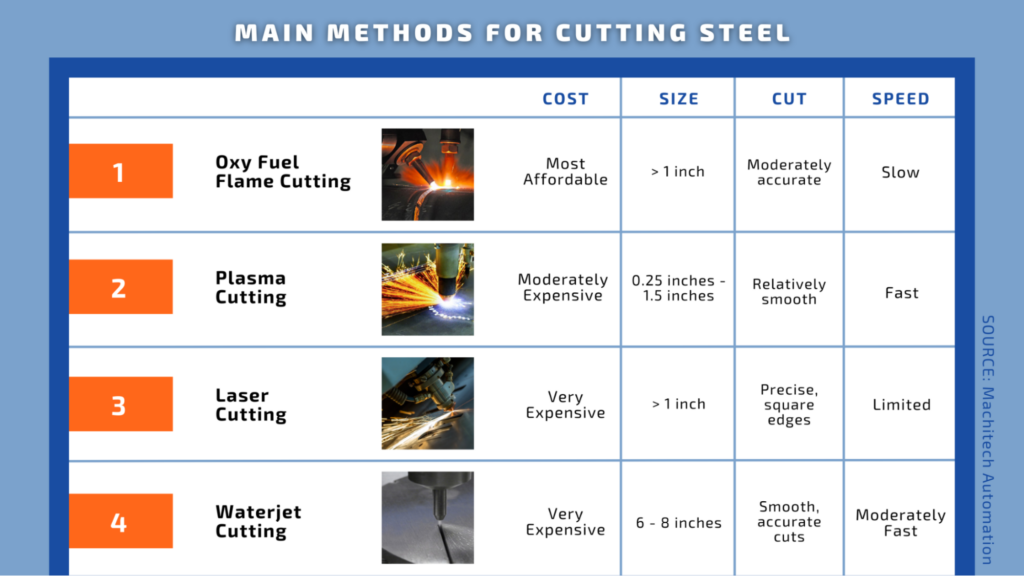
1. Oxy Fuel Flame Cutting
- Process: cuts through plate using an oxygen-fueled flame
- Primary Function: for cutting ferrous materials as little as ¼ inch thick, but typically sheets greater than 1 inch thick
- Quality of Cut: generates some slag, but the surface is relatively smooth
2. Plasma Cutting
- Process: a conductive stream of heated gas produced by a plasma torch cuts the plate
- Primary Function: for cutting thinner sheets anywhere from ¼ inch to 1 ½ inches
- Quality of Cut: results in smooth edges when cutting within the recommended range
3. Laser Cutting
- Process: a chemical reaction between iron and oxygen creates a fine laser beam that cuts through the metal plate
- Primary Function: usually for processing plates less than 1 inch thick
- Quality of Cut: capable of precise, square edges and small holes
4. Waterjet Cutting
- Process: uses a high-pressure stream of water to cut through metal plates
- Primary Function: for processing thicker metal plates up to 6-8 inches thick
- Quality of Cut: produces a smooth and accurate edge
How to Choose the Best Way to Cut Steel
Most sheet steel and plate steel requires a specific process for safe and effective cutting. So what is the best way to cut steel materials for your project?
Identifying the Proper Technique for Cutting Steel
As we know, manufacturers supply different steel varieties with varying properties. These attributes include thickness, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, grade, and reflection. Makers must consider the following properties when determining how to cut through steel for their project:
Attributes to Consider
- Thickness – How thick or thin is the steel plate material? Oxy fuel flame cutting can process plates up to 12 inches in thickness. Conversely, laser cutting is the typical choice for very thin plates.
- Precision – How precise of a cut is needed? Waterjet cutting results in a precise edge, while laser cutting is effective for creating small holes.
- Edge Quality – How clean does the edge need to be? Many steel plates require secondary processing for refining corners and edges. Plasma or laser cutting usually produces clean edges that don’t require further processing.
- Material Properties – How corrosive, conductive, or reflective is the plate you’re cutting? For example, most manufacturers prefer plasma cutting for more corrosion-resistant materials, and laser cutting can be challenging with reflective materials.
Expert Tips for How to Cut Metal Safely
Properly and safely cutting steel plates requires adequate preparation and methodology. Safety is always the priority despite the chosen cutting method. Below, Pennsylvania Steel Company offers a few tips for how to cut steel responsibly:
Remember PPE.
Gloves, goggles, masks, and headgear are just a few basic examples of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) necessary when cutting steel and other metal materials. Regardless of the selected cutting method, every project requires adequate PPE free of holes or tears.
Practice proper tool etiquette and safety.
Tools make our jobs more manageable, but only when utilized properly. Only use tools for which you’ve received training in full, and ask for assistance from a superior when needed. Furthermore, sufficiently maintain tools and replace or repair components when necessary.
Keep the work area clear.
Avoid tripping and other safety hazards by clearing the immediate work area of any clutter. Keeping tools and materials organized and out of the way ensures a productive workspace for everyone.
Turn to Pennsylvania Steel Company for Steel Plate Supply & Processing
After browsing the various cutting steel plate methods, weigh which techniques are most appropriate for your project’s scope. Generally, the best way to cut steel is the safest method. Our experienced metal distributors employ decades of industry knowledge to ensure our customers receive only premium metal supplies and services.
From North Carolina to New York, Pennsylvania Steel Company provides top-notch metals to fabricators and manufacturers at our New England/New York, Pennsylvania, the Southeast, and Ohio steel warehouses. Contact the sheet plate distributors at Pennsylvania Steel Company today for fast delivery options for your steel plate project.